Court Structure in Malaysia
Case management which is largely undertaken by the judges is a central feature that enhances the performance of these courts. Commercial matters although to a lesser extent are also heard and dealt with in other parts of Malaysia where the High Courts enjoy local jurisdiction 1.

Malaysian Criminals Go To Different Courts Depending On Asklegal My
The judiciary additionally gives a mechanism for the resolution of disputes.

. The Court of Appeal was first introduced in the hierarchical structure of courts in Malaysia in 1994. There are also various other courts outside of the hierarchy. Before 1969 the High Court in Singapore was also part of the Malaysian courts system see Law of Singapore.
The Juvenile Court is paralleled in jurisdiction with the Magistrates Court. Article 121 of the Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two High Courts of coordinate jurisdictionthe High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak before 1994 the High Court in Borneo. The hierarchy of courts begins from the Magistrates Court Sessions Court High Court Court of Appeal and finally the Federal Court.
The highest position in the judiciary of Malaysia is the Chief Justice of t he Federal. The judicial system in Malaysia is a federalized court system operating uniformly throughout the country. The jurisdiction of the courts in civil or criminal matters are contained in theSubordinate Courts Act 1948 and the Courts of Judicature Act 1964.
Executive Executive power is vested in the cabinet led by the prime minister. Outside the court hierarchy are the Syariah Courts Penghulus Courts and the Native Courts. The Federal Court is the supreme court.
A Magistrates Court and a Court for Children are presided by magistrates. The Federal Court of Malaysia Malay. Normally the Federal Court sits at the Palace of Justice in Putrajaya.
Malaysia has a bound together legal framework and all courts take awareness of both federal and state laws. It is the final court of appeal and it has exclusive jurisdiction in constitutional matters and in issues arising between states or between the federal government and states. However the High Court of Singapore remained part of the Malaysian Federal Court structure until 1969 when Singapore enacted the Supreme Court of Judicature Act to regularise the judicial system.
Thus this creates two separate local jurisdiction of the courts for Peninsular Malaysia and for East Malaysia. The High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court are superior courts while the Magistrates Court the Court for Children and the Sessions Court are subordinate courts. Article 121 of the Constitution of Malaysia provides that there shall be two High Courts of coordinate jurisdictionthe High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak before 1994 the High Court in Borneo.
Establishment seeks to create additional channels for appeal cases heard by the High Court and also to reduce the burden on the Federal Court to hear appeal cases brought before it. However the Federal Court also goes on circuit to the major towns of Penang Ipoh Kota Bharu Johor Bahru Alor Setar Kuantan Malacca Kuching and Kota Kinabalu section 75 of. Upon the declaration of independence of the Federation of Malaya on 31 August 1957 the Malayan Court System was structured into the Superior Courts and the Subordinate Courts.
The High Court Court of Appeal and the Federal Court are superior courts. High Courts are located in Peninsular Malaysia and in SabahSarawak. The Magistrates Court the Court for Children and the Sessions Court are subordinate courts.
Before 1969 the High Court in Singapore was also part of the Malaysian courts system see Law of Singapore. The Commercial Courts are situated in Kuala Lumpur. The Superior Courts consisted of the High Court of Malaya and a court of appeal termed the Federal Court.
The judiciary which is also known as the judicial system or court system is the arrangement of courts that decodes and applies the law for the state. The Malaysian constitution stipulates that the prime minister must be a member of the Lower House of parliament who in the opinion of the Yang di-Pertuan Agong. Mahkamah Persekutuan Malaysia is the highest court and the final appellate court in Malaysia.
Referred Statutes - Federal Constitution of Malaysia - Courts Judicature Act 1964 - Subordinate Courts Act 1948 - Industrial Relations Act 1967 - Child Act 2001 Introduction - Superior Courts Federal Court Court of Appeal and The two High Courts are Superior Courts Art 121 of Federal Constitution Courts of Judicature Act 1964 Unlimited Jurisdiction -. Article 121 of the Constitution provides for two High Courts of co-ordinate jurisdiction the High Court in Malaya and the High Court in Sabah and Sarawak. The hierarchy of courts begins from the Magistrates Court Sessions Court High Court Court of Appeal and finally the Federal Court.

Malaysian Criminals Go To Different Courts Depending On Asklegal My
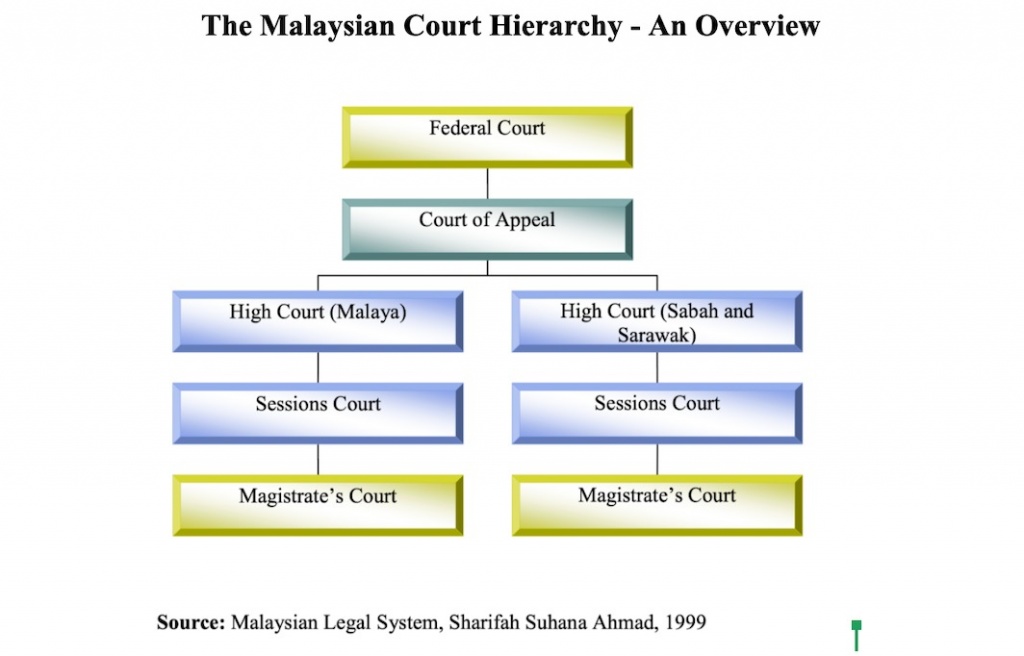
The Malaysian Court Hierarchy A Review Of Malaysia S Civil And Criminal Court Hierarchy Richard Wee Chambers
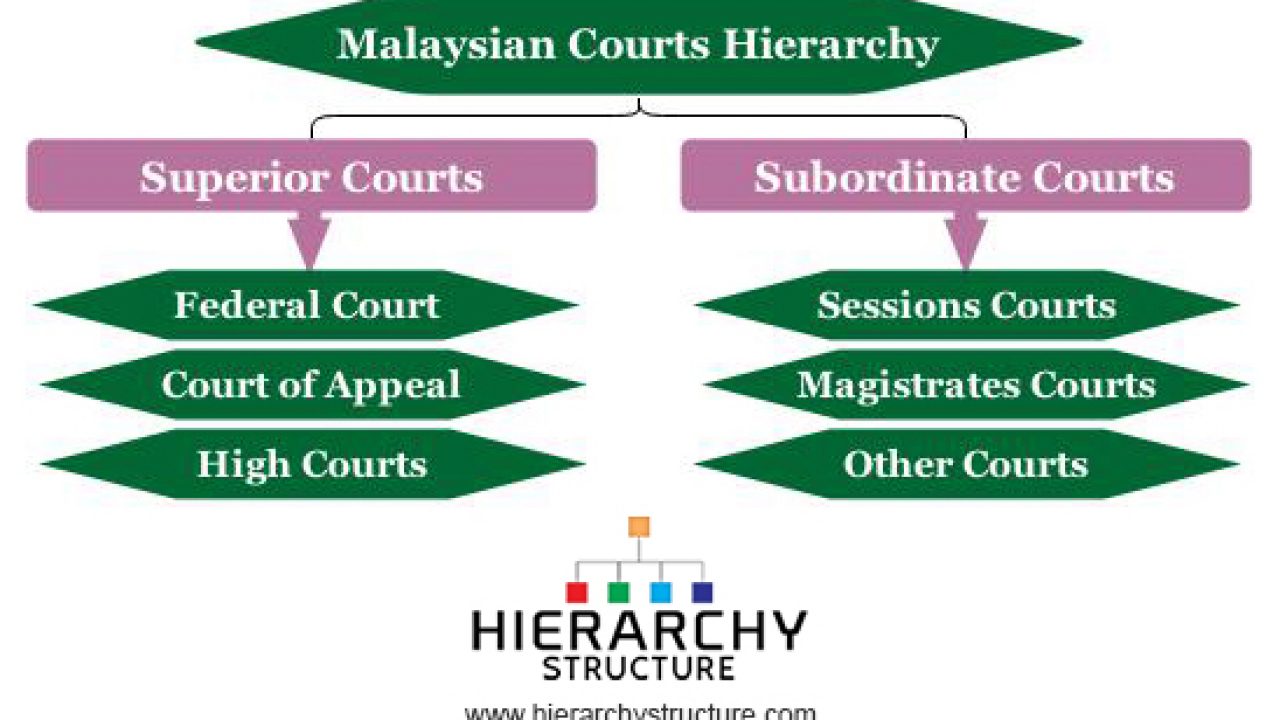
Malaysian Courts Hierarchy Chart Hierarchystructure Com

The Malaysian Court System Asklegal My

Hierarchy Portal Rasmi Pejabat Ketua Pendaftar Mahkamah Persekutuan Malaysia
Comments
Post a Comment